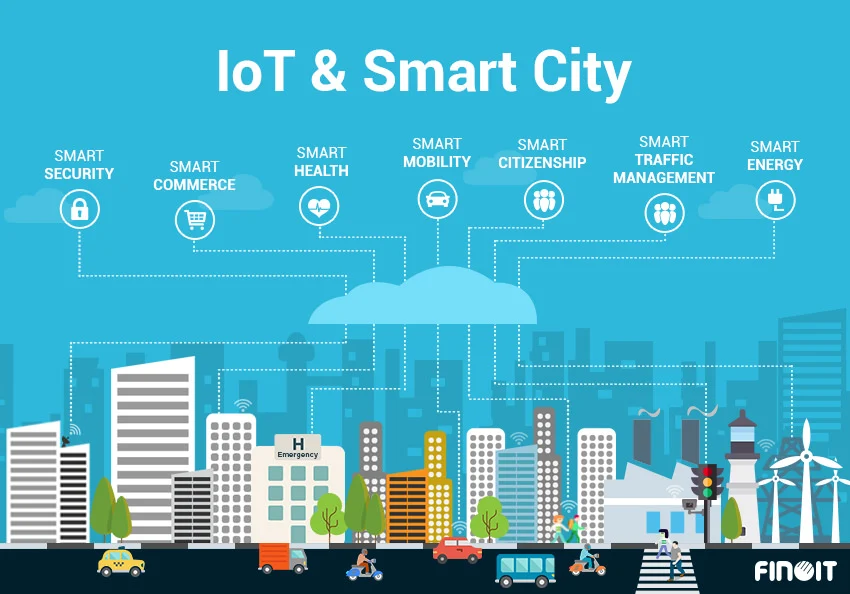
The Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a futuristic concept—it's transforming urban landscapes into intelligent, connected ecosystems. As cities worldwide face growing populations and infrastructure challenges, IoT emerges as a powerful solution to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban environments.
What Makes a City "Smart"?
A smart city leverages IoT technology to collect and analyze data from connected devices, enabling better decision-making and resource management. Key components include:
- Connected Infrastructure: Sensors embedded in roads, buildings, and utilities monitor conditions in real-time.
- Data Analytics: Advanced algorithms process vast amounts of data to optimize city operations.
- Citizen Engagement: Mobile apps and digital platforms keep residents informed and involved.
- Sustainability: Smart energy grids and waste management reduce environmental impact.
IoT Applications in Smart Cities
1. Intelligent Traffic Management
IoT-enabled traffic lights and sensors optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve emergency response times. In Barcelona, smart traffic lights have reduced travel times by 21% and emissions by 20%.
2. Smart Energy Grids
Connected sensors monitor energy consumption patterns, allowing for dynamic pricing and better load management. Amsterdam's smart grid project has helped reduce energy consumption by 14% across participating households.
3. Waste Management
Smart bins with fill-level sensors optimize collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs. Seoul's smart waste management system has decreased collection costs by 83%.
4. Public Safety
Connected cameras and environmental sensors enhance public safety by detecting accidents, monitoring air quality, and predicting potential hazards. Chicago's Array of Things project collects real-time data on the city's environment and infrastructure.
Challenges in Implementing Smart City IoT
While the benefits are clear, cities face several challenges in IoT implementation:
- Data Privacy: Balancing data collection with citizen privacy rights.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Interoperability: Ensuring different IoT systems can communicate effectively.
- Infrastructure Costs: Significant upfront investment required for deployment.
The Future of Smart Cities
As 5G networks expand and AI becomes more sophisticated, we can expect even more advanced IoT applications:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars communicating with traffic systems and each other.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicting infrastructure failures before they occur.
- Personalized Urban Services: Hyper-local services tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of cities for simulation and planning.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT in urban development represents a fundamental shift in how we design, build, and manage cities. While challenges remain, the potential benefits—from reduced environmental impact to improved quality of life—make smart city initiatives a critical component of our urban future. As technology continues to evolve, the cities of tomorrow will be more connected, efficient, and responsive than ever before.

Emily Chen
IoT Solutions Architect at Conneural
Emily specializes in designing and implementing IoT solutions for smart cities. With over 8 years of experience in urban technology, she helps municipalities leverage connected devices to create more sustainable and efficient urban environments.